Contents
Summary
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a kind of bio-based and biodegradable polymer material, which is produced from starch fermentation to generate lactic acid, and then polymerized to get PLA, which can be completely degraded to CO₂ and H₂O after use.PLA has the advantages of non-toxicity and the degradation products can be involved in the human body metabolism, which has been widely used in the field of medical treatment.Another advantage of PLA is the production process with low energy consumption and low carbon emission. It can be seen that the production and use of PLA can not only alleviate the serious Baise pollution, but also save oil resources.
PLA is a new type of polymer material, and its chemical structure formula is shown in Figure 2-1.
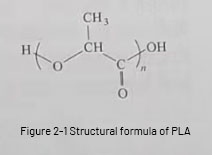
The process of PLA production is: extract starch from plants, starch is decomposed by enzymes to get glucose, lactic acid is produced by lactobacillus fermentation, and PLA is obtained by chemical synthesis.The recycling of PLA-type wastes is green and environmental friendly, and it can be decomposed into CO₂ and H₂O completely by microorganisms, water, acid or alkali, and will not cause pollution to the environment.
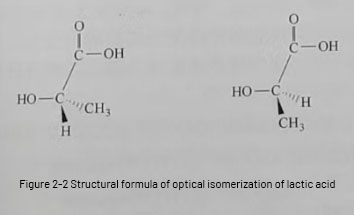
The structural unit of PLA is lactic acid. Lactic acid monomer was first found to exist in milk in 1780, also known as a-hydroxy acid or 2-hydroxypropionic acid, which is an organic acid with chiral carbon, and usually behaves as a colorless liquid with hygroscopicity, and according to the optical activity, it can be divided into levolactic acid (L-lactic acid) and dextro-lactic acid (D-lactic acid), and its structural formula is shown in Fig. 2-2. lactic acid can form racemic lactic acid (DL lactic acid). Among them, D-lactic acid exists in human muscle tissue, and L-lactic acid is a mammalian metabolite.
Synthesis and method of polylactic acid
Since there is no natural PLA in nature, PLA can only be obtained by artificial synthesis, and currently the main methods used to synthesize PLA are lactic acid direct polycondensation, propylene glycol ester ring-opening polymerization, reactive extrusion polymerization, direct solid-phase polymerization, solution polymerization, etc. The following is a description of lactic acid direct polycondensation, propylene glycol ester ring-opening polymerization, direct solid-phase polymerization, and solution polymerization. The following is an introduction to the direct polycondensation of lactic acid and the ring-opening polymerization of propylene glycol.
Direct Polycondensation
Dehydration polycondensation of lactic acid is the first simple and effective method for the preparation of PLA. Lactic acid molecules contain both carboxyl and hydroxyl, carboxyl and hydroxyl have high reactivity, by heating, lactic acid molecules between the dehydration condensation reaction can be directly prepared to get the PLA. direct polycondensation method has a wide range of raw materials, low price, easy to operate, the use of reagents and so on, but the polymer relative molecular mass is low, is not enough to meet the demand of the market of the film or spinning, application of the value is not great, must further improve the relative molecular mass of the polymer to open up a broader market, so that it has a broader market. However, the relative molecular mass of the polymer is low, which is not enough to meet the market demand of film-forming or spinning, and the application value is not large. Based on the above shortcomings of the synthetic PLA, two methods have been proposed to improve it; ① melt – solid phase polycondensation method, with high purity lactic acid monomer as the raw material for the reaction, through the melt polymerization method to prepare a low relative molecular mass of PLA, and then use solid phase polymerization method, so that the end group of the PLA of a lower relative molecular mass of the end group of the further reaction of the expansion of the chain, which greatly improved the relative molecular mass of the final product; ② chain extension Quality; ② chain expansion method, lactic acid monomer as raw material, the first direct condensation synthesis of low relative molecular mass of PLA, and then heated to melt under ammonia protection (temperature of about 200℃) and add isocyanate chain expansion, the relative molecular mass can be increased by 3 to 4 times.
Propylene glycol ester ring-opening polymerization method
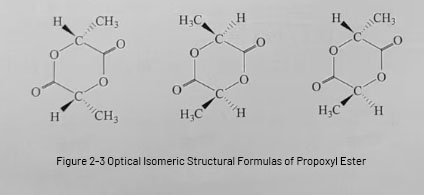
When PLA is prepared by direct dehydration and condensation of lactic acid, the viscosity of the reaction system gradually increases during the reaction process, which makes it difficult to separate the water produced by the reaction and prevents the reaction from proceeding in the positive direction, resulting in a low relative molecular mass of PLA, which is insufficient to meet the market demand. Therefore, we need to use more feasible methods to improve the relative molecular mass of PLA, propylene glycol ester ring-opening polymerization method can produce high relative molecular mass of PLA. propylene glycol ester ring-opening polymerization of PLA is divided into two steps: ① lactic acid in the role of the catalyst, the dehydration of the dimer – propylene glycol ester; ② propylene glycol ester directly melt polymerization of the body to get the PLA. the method of the first step of the system will be in the system of all water is removed, and the second step of the reaction for the body of the melt polymerization. In this method, all the water in the system is removed in the first step, and the reaction in the second step is a native reaction, which does not produce any impurity that hinders the reaction, so PLA with high relative molecular mass can be obtained.The optical isomeric structure of the propylene glycol ester is shown in Fig. 2-3. Under certain conditions, either lactic acid condensation or propylene glycol ester ring-opening can be obtained full-regulated, inter-regulated, hetero-regulated and atactic PLA. the mechanism of propylene glycol ester ring-opening polymerization can be divided into: anionic ring-opening polymerization, cationic ring-opening polymerization and ligand-type ring-opening polymerization.
In summary, although there are various methods for the synthesis of PLA, propylene glycol ester ring-opening polymerization (PGP) is the most effective and widely used synthesis method to obtain PLA with high relative molecular mass (RMM) greater than 100,000 RMM.

